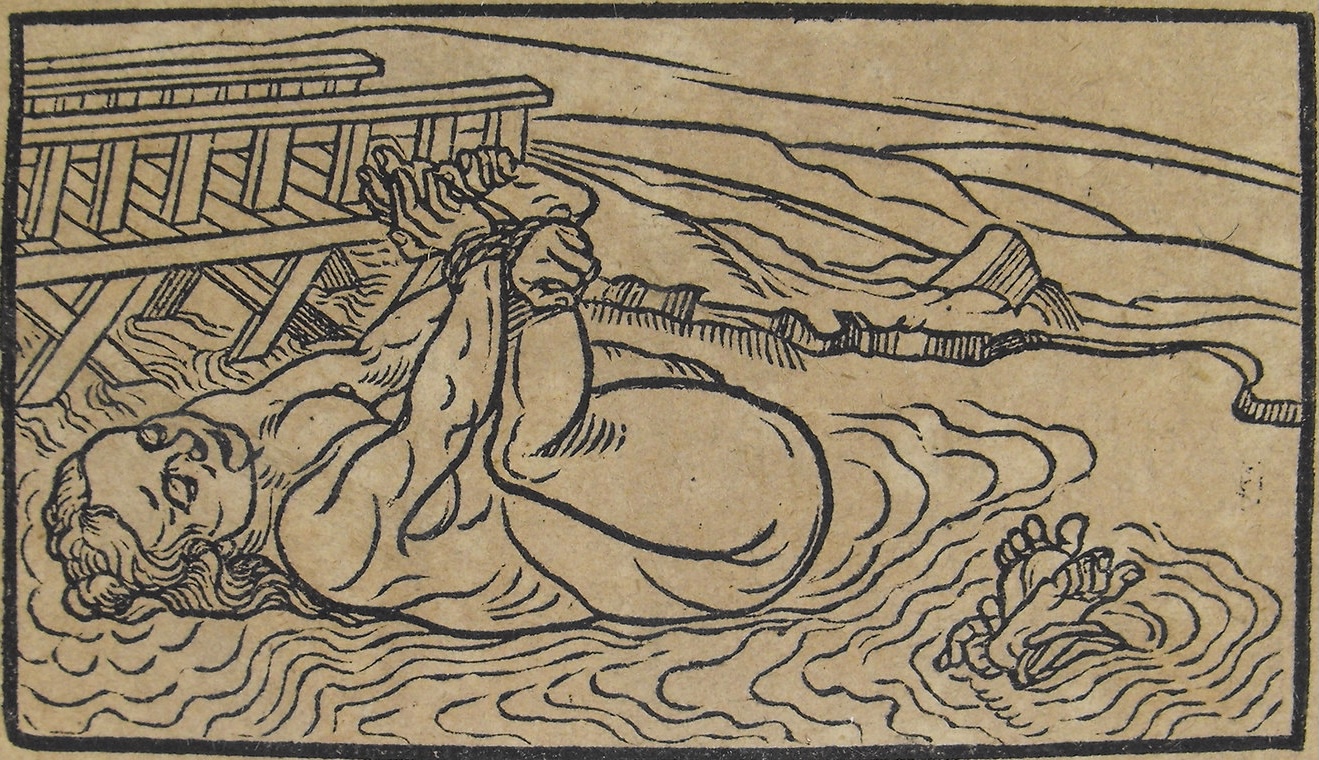
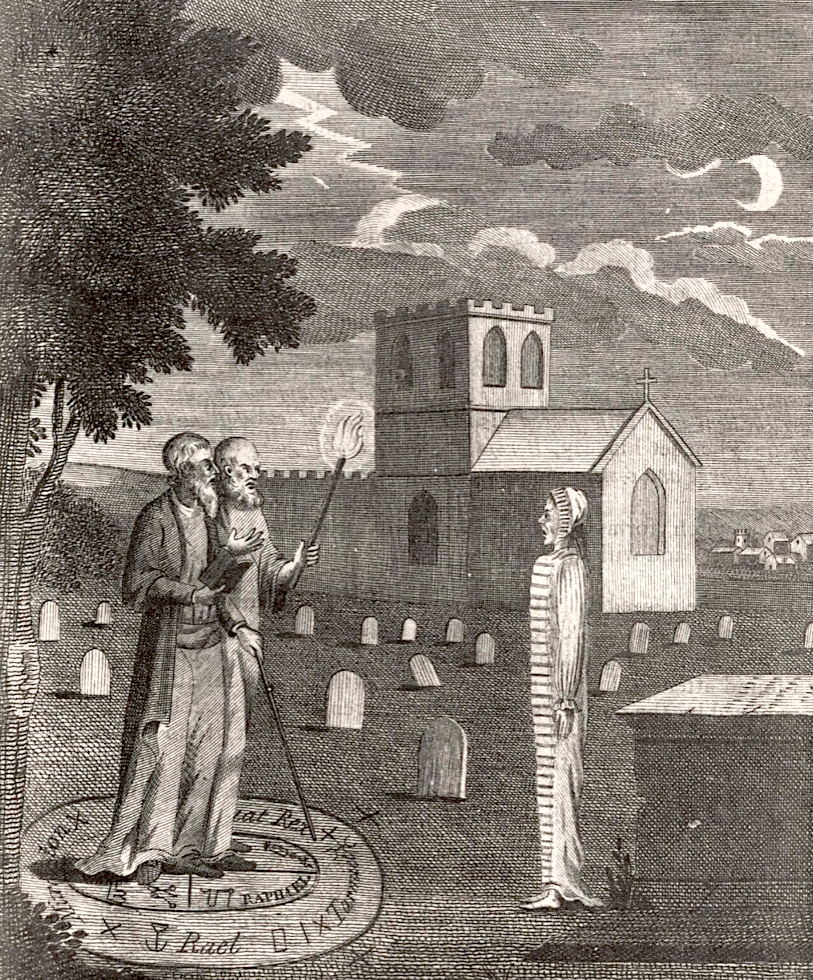
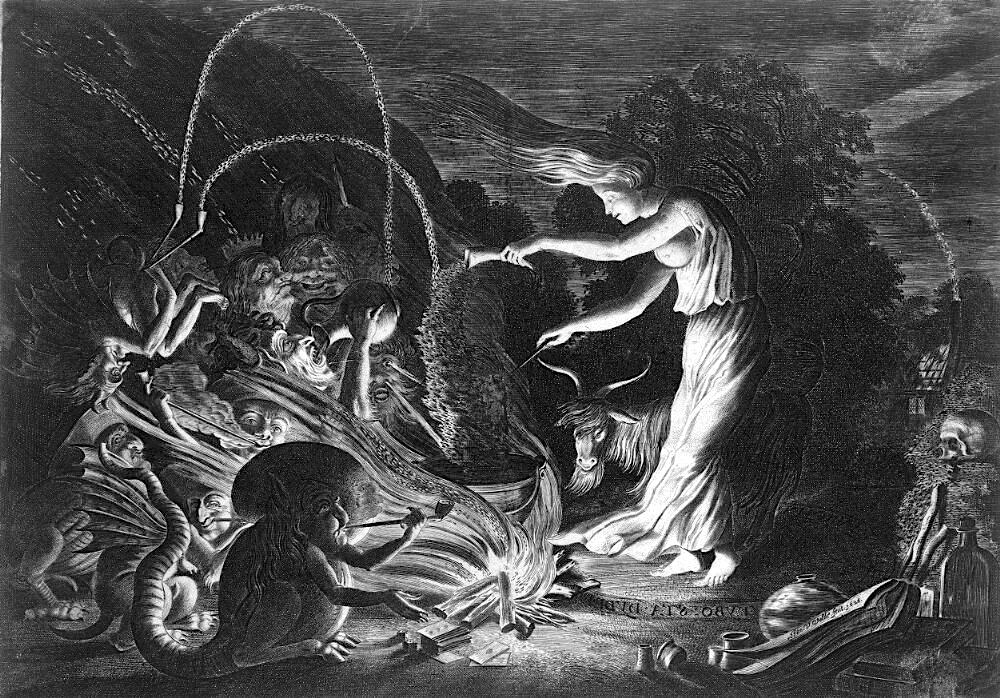
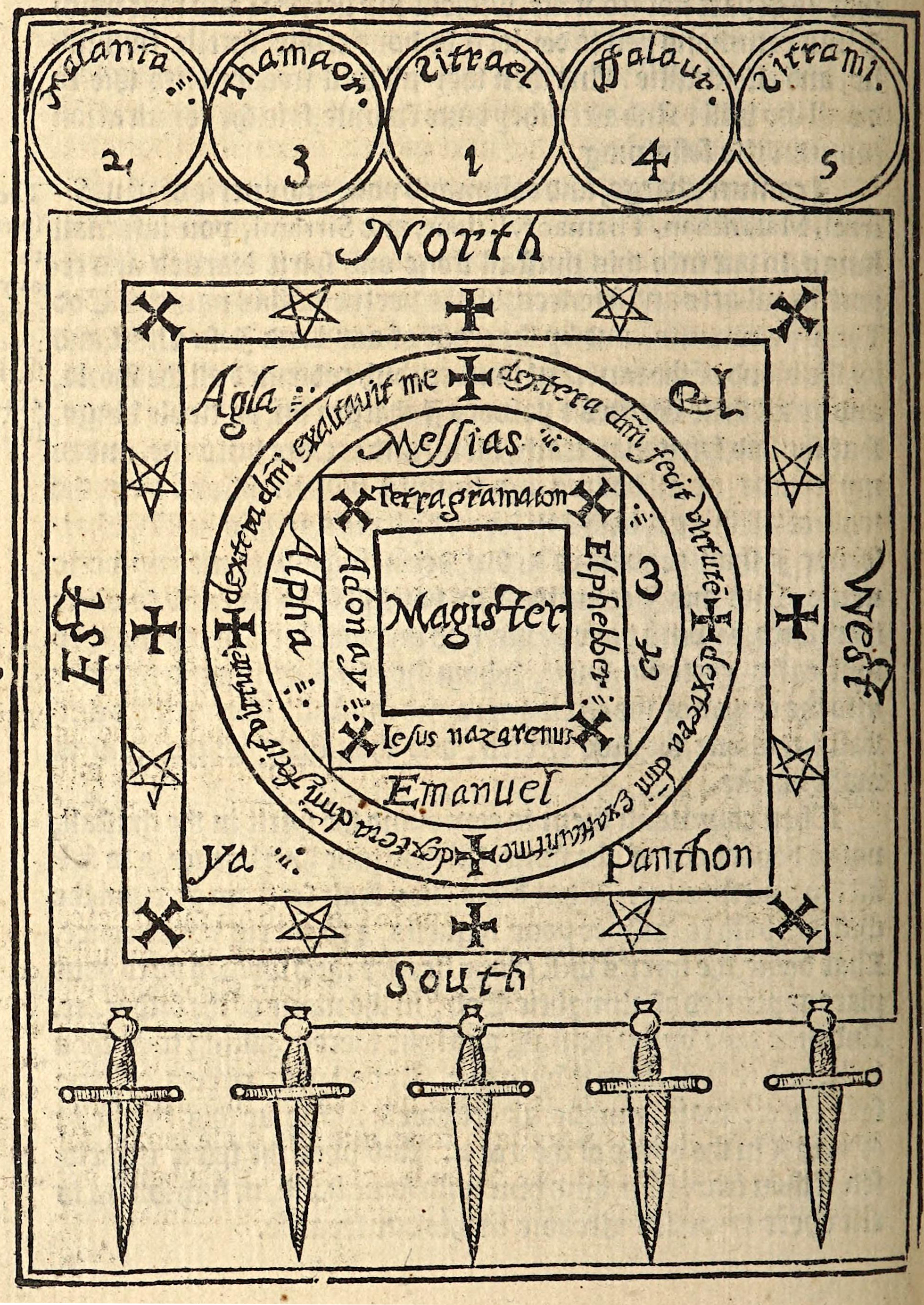
In the 16th and 17th century, women accused of witchcraft were often subjected to a trial by water. Their hands were bound and they were thrown into water. If they floated—a witch. If they sunk—innocent. While they often had rope tied around their waists to bring them back, there were many accidental drownings. From: Bericht von Erforschung, Herman Neuwaldt, 1611. Source: University of Glasgow Library