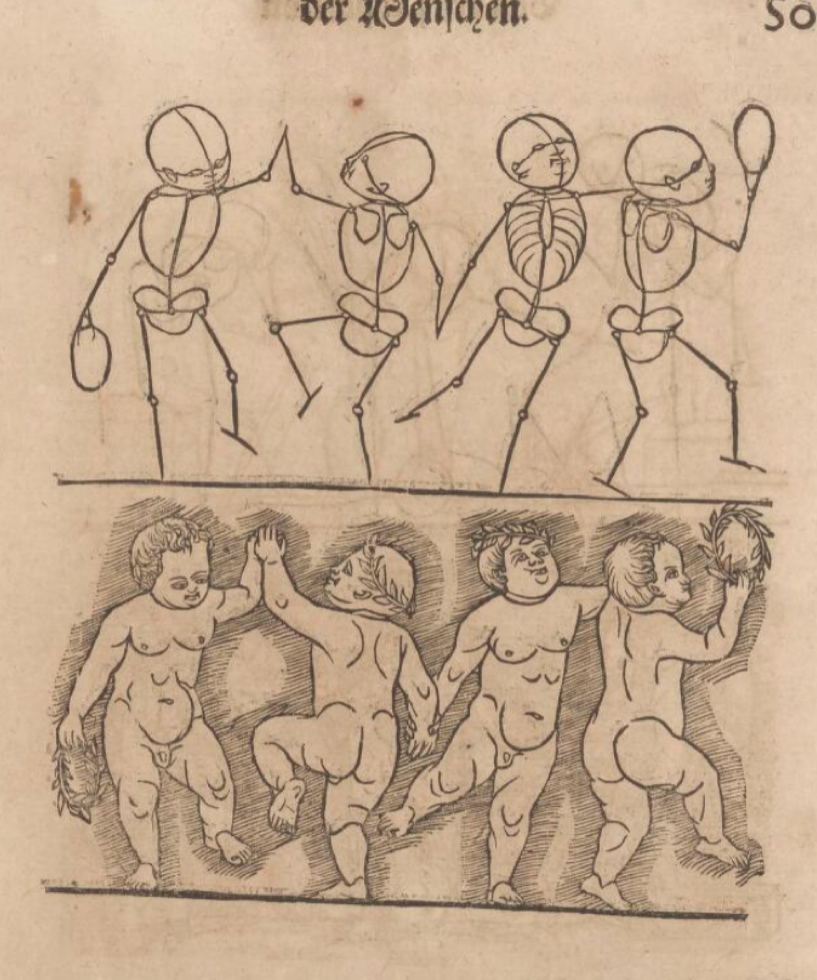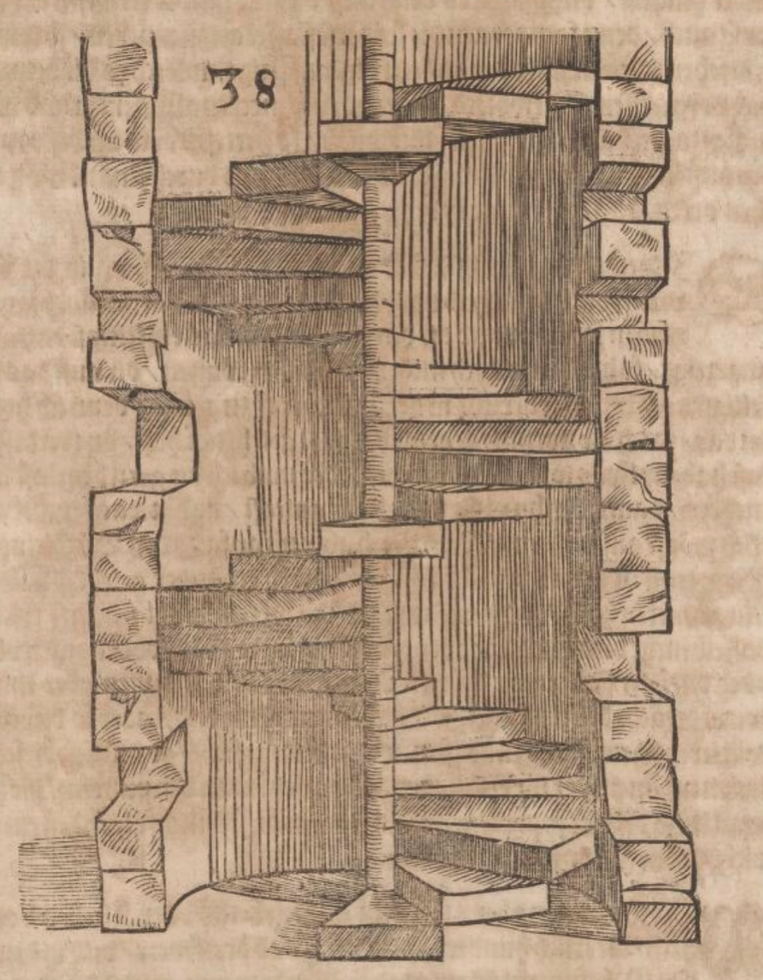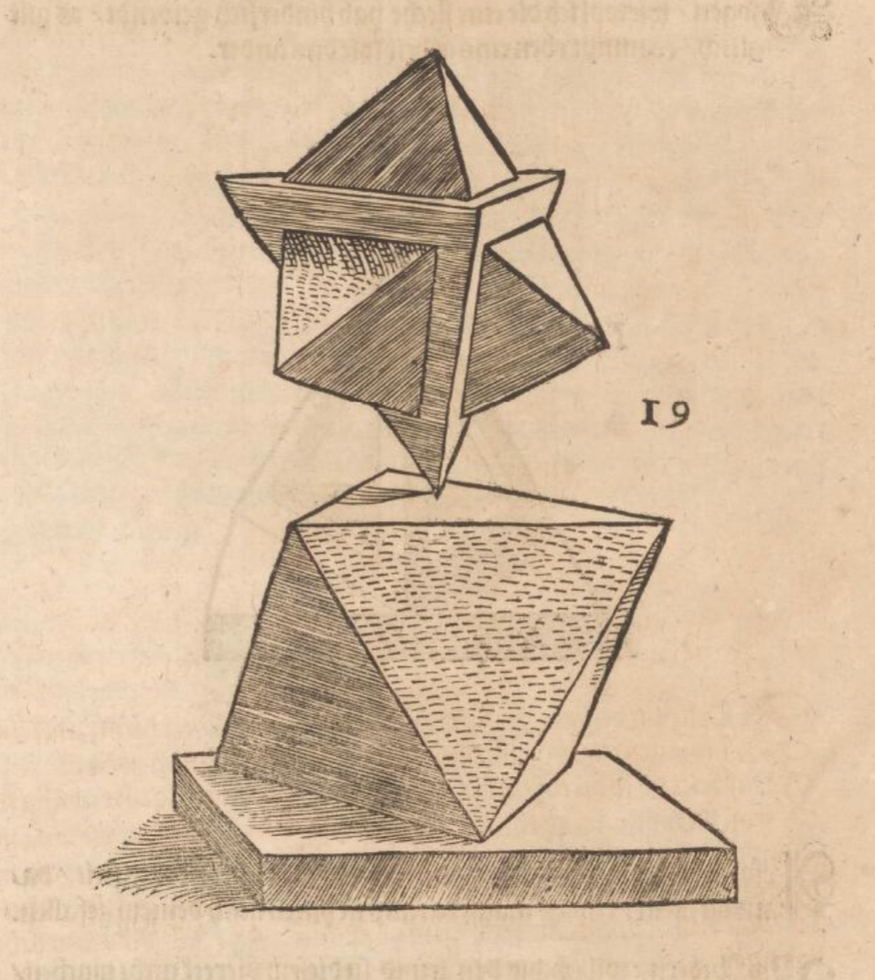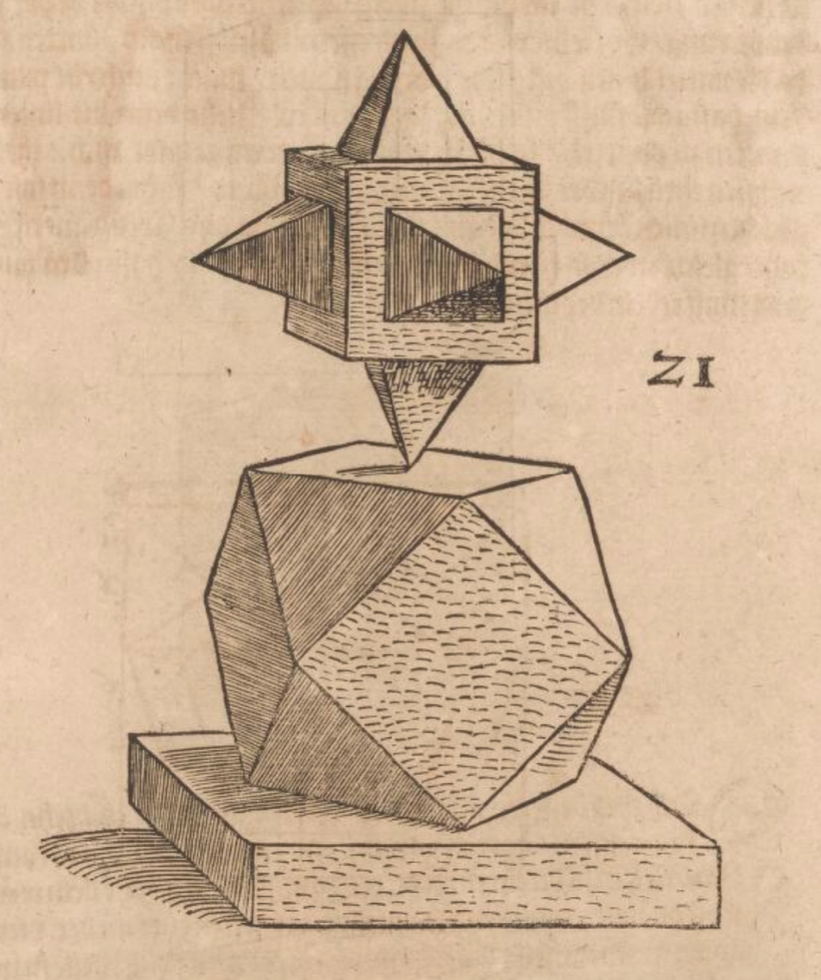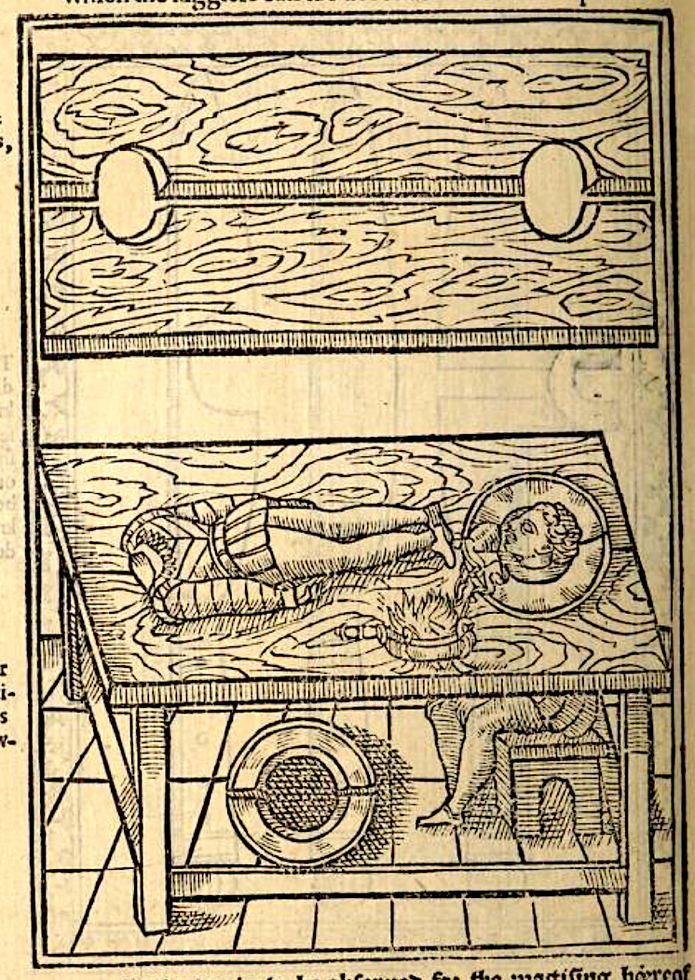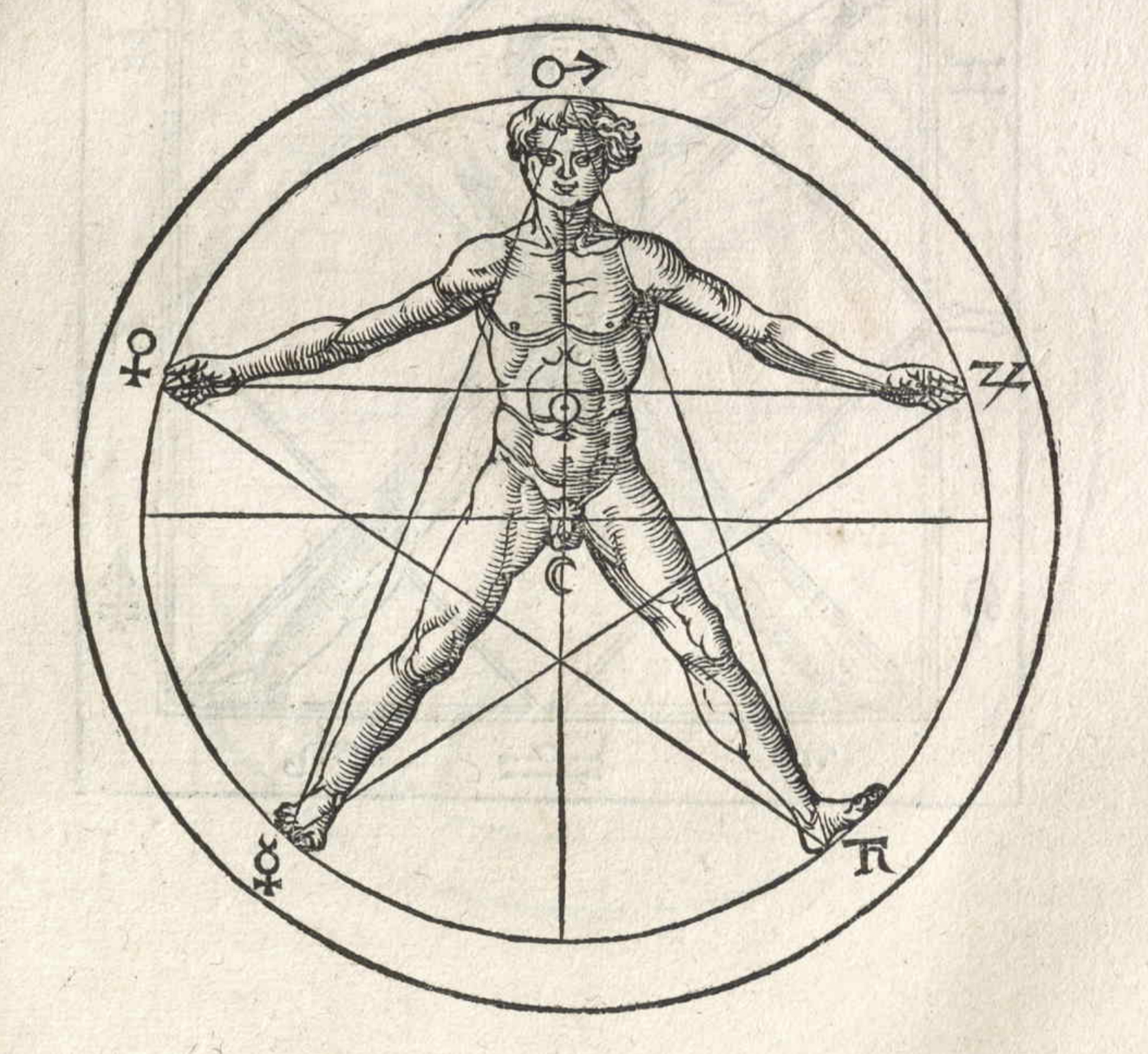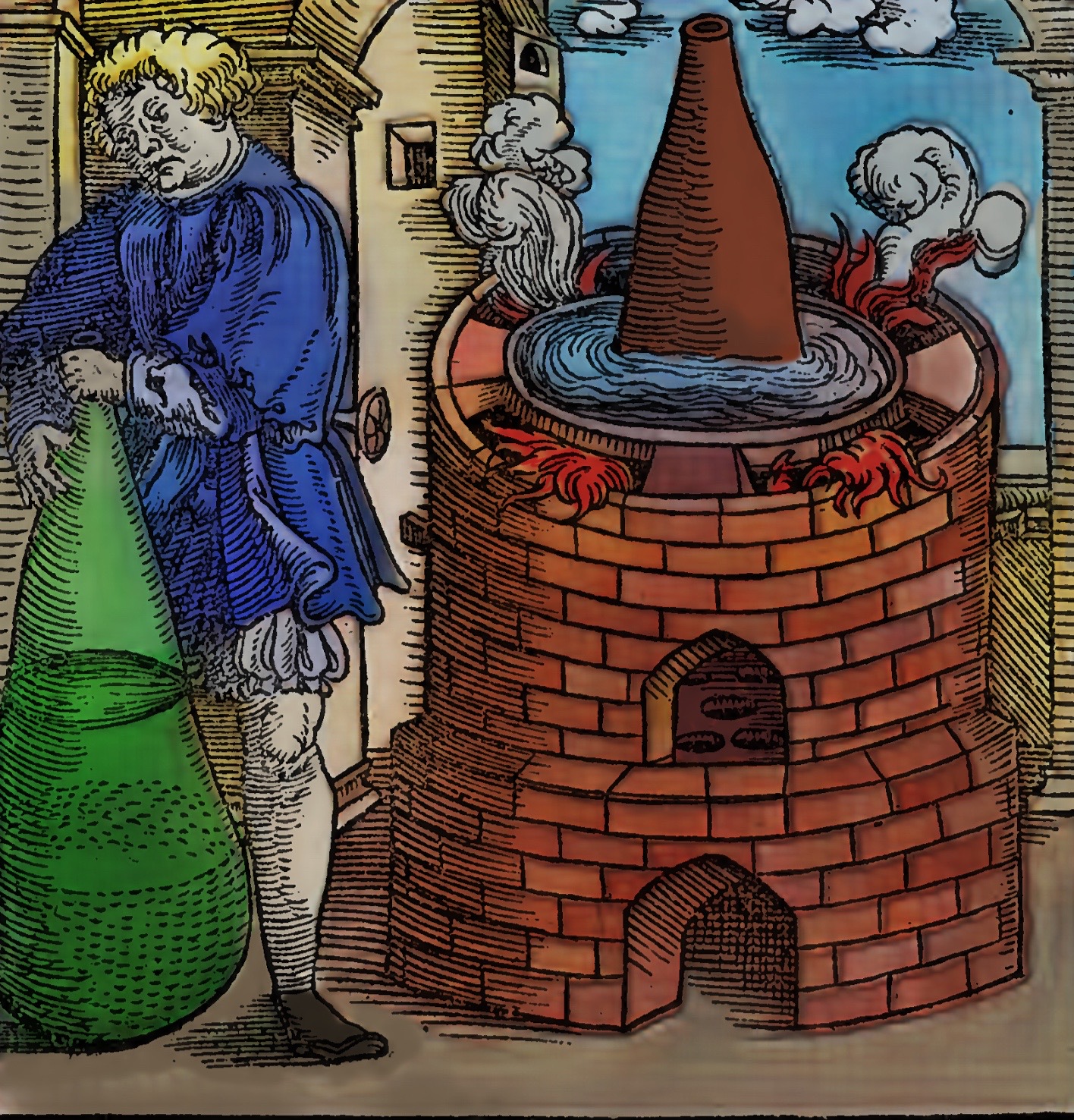
Woodcuts from Des Circkelsz und Richtscheyts, Heinrich Lautensack, 1618. This book was meant as a guide for painters, sculptors, stonemasons, goldsmiths, and others to better understand perspective and the human form. Source: Embassy of the Free Mind