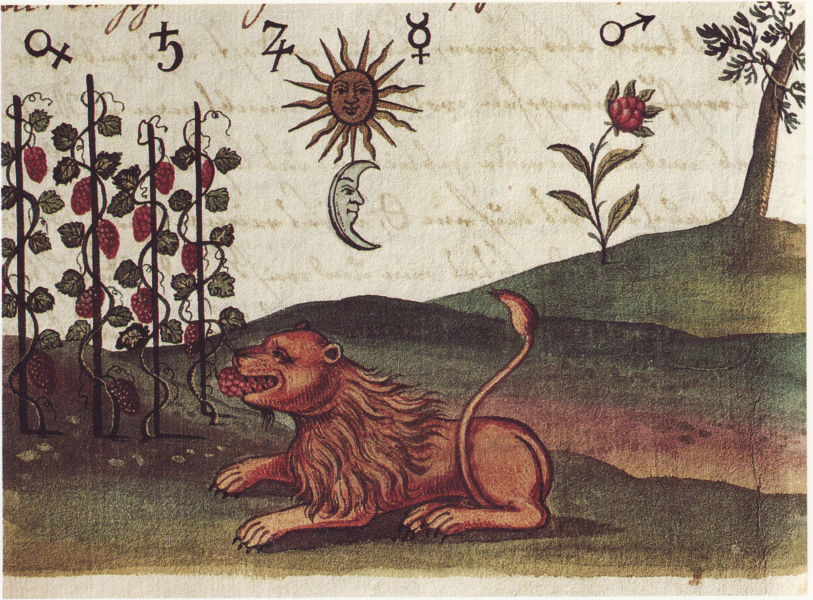
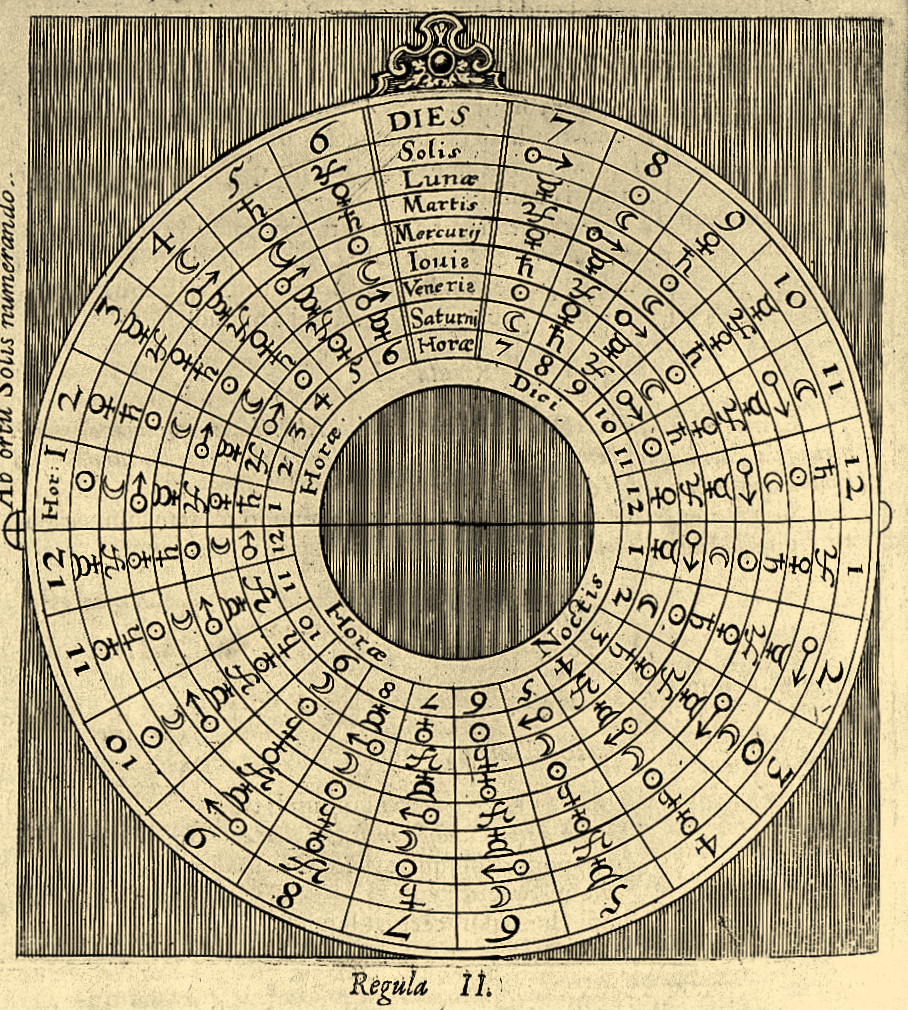
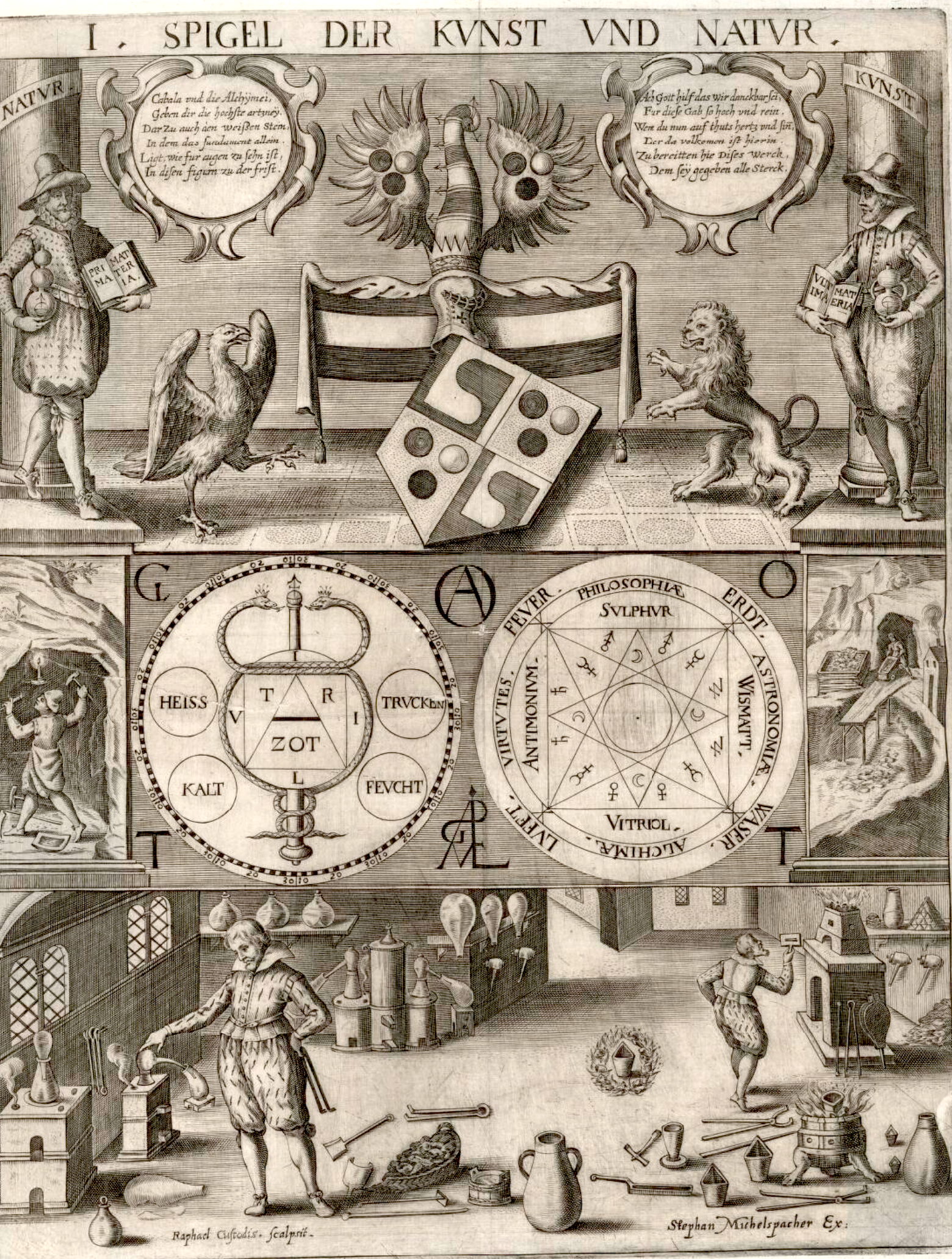
Heavenly bodies are essential in alchemy, particularly the sun, moon, Venus, Mars, Mercury, Jupiter and Saturn. Symbols of these planets are common in alchemical art along with their Greek god counterparts, and the success of operations were sometimes tied to zodiacal time. Beyond times of the month, day and hour, these heavenly bodies also corresponded to metals, parts of the body, cardinal sins, and cardinal virtues. Images: Clavis artis, Zoroaster, 17th century and De naturae…historia, Robert Fludd, 1680