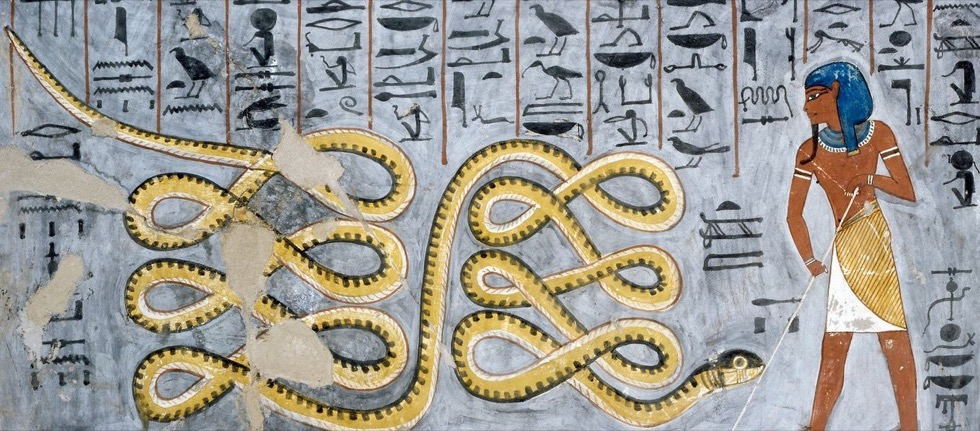
The Book of Thoth is a name given to a number of books purported to be written by Thoth, the Egyptian God of Knowledge. One version of the book is described in the ancient story Setne I. In the story, the book contained two spells—a spell to speak to animals, and one to perceive the gods. The book was originally hidden at the bottom of the Nile, locked and guarded by serpents, until it was retrieved by Prince Neferkaptah. As punishment, he was driven to suicide and entombed with the book. Years later, Prince Setne Khamwas retrieves the book from Neferkaptah’s tomb. The prince is seduced by the illusion of a beautiful woman who convinces him to kill his children, and make a fool of himself in front of the Pharaoh. Prince Setne returns the book in fear of further punishment. Image: Hunefer’s Book of the Dead, detail with Thoth